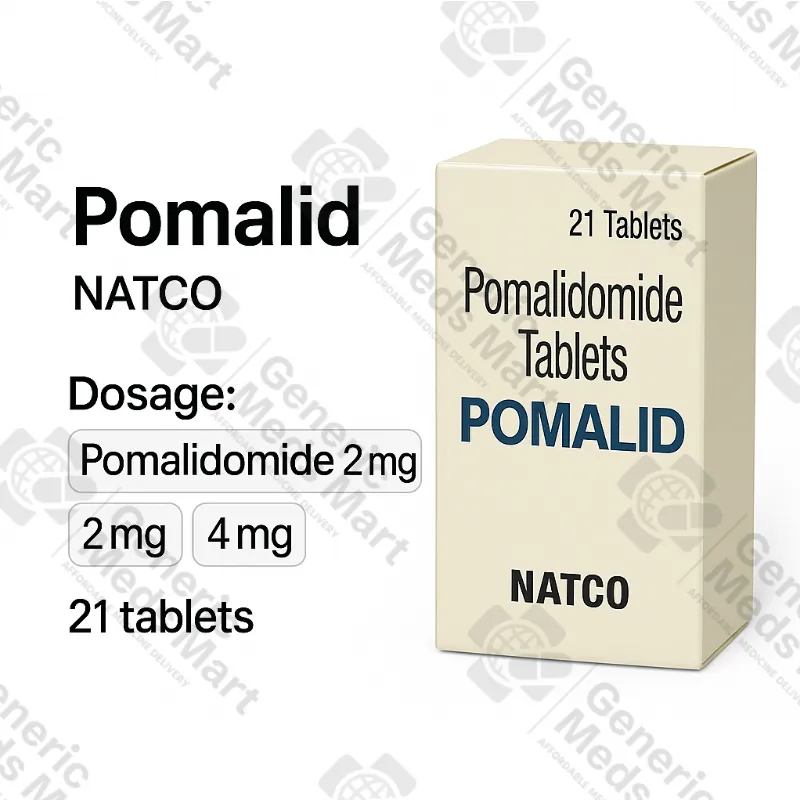
Pomalid 2 mg, 4 mg Pomalidomide Capsules
$276.00 – $499.00Price range: $276.00 through $499.00
Pomalid is an oral immunomodulatory medicine containing pomalidomide, used with dexamethasone in adults with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma after prior therapies. Pomalid 2 mg and 4 mg capsules (1 pack / 21 tabs each strength) allow haematologists to individualise pomalidomide dosage across 21-day treatment cycles, and Generic Meds Mart supplies both strengths in original packaging from licensed distributors with discreet, trackable international shipping where regulations allow.
Buy Pomalid 2 mg and 4 mg Pomalidomide Capsules Online
Pomalid 2 mg and 4 mg Pomalidomide Capsules (1 pack / 21 tabs)
At a Glance
Generic Name: Pomalidomide
Brand Name: Pomalid
Strength & Pack Size: 2 mg and 4 mg pomalidomide capsules; 1 pack / 21 capsules each strength
Dosage Form & Route: Oral capsules taken by mouth once daily on treatment days
Therapeutic Class: Immunomodulatory agent (IMiD) for haematologic malignancy
Primary Indication: Relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma in adults after prior therapies
Usual Regimen: 21-day pomalidomide course in a 28-day cycle with dexamethasone, as defined by a haematologist
Prescription Status: Prescription-only cytotoxic / immunomodulatory medicine
Storage: Store at room temperature below 25 °C in the original blister pack, away from children
Product Description
Pomalid is a pomalidomide-based oral anticancer medicine used together with dexamethasone in adults with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma who have previously received other treatments. Each pack of Pomalid 2 mg or Pomalid 4 mg contains 21 capsules, corresponding to a typical 21-day treatment period within a 28-day cycle when pomalidomide is taken once daily on treatment days. The availability of both 2 mg and 4 mg strengths allows haematologists to individualise the pomalidomide dosage, starting with a standard daily dose and then adjusting up or down depending on tolerability, blood counts and other clinical factors.
Multiple myeloma is a malignant disease of plasma cells in the bone marrow, and many patients will need a series of different regimens over time. Pomalidomide belongs to the immunomodulatory class of drugs (IMiDs) that help the immune system recognise and attack abnormal plasma cells, while also exerting direct anti-myeloma effects. Pomalid capsules are not used alone; they are given in combination with dexamethasone and sometimes with other agents as part of a comprehensive treatment plan designed by a myeloma specialist.
Generic Meds Mart supplies Pomalid 2 mg and 4 mg pomalidomide capsules in original manufacturer packaging sourced from licensed distributors. Each blister strip and outer carton clearly displays the strength, generic name, capsule count, batch number, expiry date and storage instructions so that hospital and clinic pharmacies can verify the product against your prescription. Shipments are prepared in discreet outer packaging that does not mention multiple myeloma, pomalidomide or oncology, supporting privacy while you access medicines prescribed by your haematology team.
Key Uses
Pomalid is used in adults with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma, typically after at least two prior lines of therapy that may have included agents such as lenalidomide and bortezomib. It is most often combined with dexamethasone and may be part of more complex regimens in some centres. The goal of pomalidomide-based therapy is to further reduce myeloma activity, control symptoms such as bone pain or anaemia and prolong progression-free survival when previous treatments are no longer effective or appropriate.
The decision to use pomalidomide, and to select Pomalid specifically, depends on a detailed assessment of prior treatments, response durations, cytogenetic risk, comorbidities, kidney function, infection risk and patient preferences. Pomalid is not appropriate for every person with myeloma, particularly those with significant uncontrolled infections, severe cytopenias or contraindications to immunomodulatory agents. Treatment should only be started and supervised by haematologists experienced in managing multiple myeloma and the safety profile of pomalidomide.
How Pomalidomide Works in Chemotherapy
Pomalidomide, the active ingredient in Pomalid capsules, is an immunomodulatory agent closely related to thalidomide and lenalidomide. It exerts its anti-myeloma effect through several mechanisms. Pomalidomide enhances the immune system’s ability to recognise and attack myeloma cells by stimulating certain T-cell and natural killer cell functions. It also promotes the degradation of specific proteins in myeloma cells via the cereblon E3 ubiquitin ligase complex, leading to changes in transcription factors that are important for myeloma cell survival.
In addition, pomalidomide has anti-angiogenic properties that can reduce the formation of new blood vessels supporting tumour growth and may disrupt the interactions between myeloma cells and the bone marrow microenvironment. By combining these immune, anti-proliferative and microenvironmental effects, pomalidomide helps to slow or reduce myeloma cell growth when used as part of combination therapy. However, because it also affects normal immune and haematopoietic cells, careful monitoring and dose adjustments are often required.
Dosage & Administration
Pomalid pomalidomide dosage and schedule must always be defined by a haematologist based on local protocols and the individual patient profile. A common approach is to give pomalidomide once daily on days 1–21 of a 28-day cycle, in combination with dexamethasone on specific days of the same cycle. The 4 mg capsule is often used as the standard starting daily dose in suitable adults, with dose reductions to 3 mg, 2 mg or 1 mg made in response to side effects, low blood counts or organ function changes. The 2 mg strength provides flexibility for these reduced-dose schedules.
Pomalid capsules should be swallowed whole with water, at roughly the same time each day, and should not be opened, crushed or chewed. Because pomalidomide can cause serious birth defects, strict pregnancy prevention and handling precautions are required. If a dose is missed, your clinic will advise whether you should skip it and resume the next day or take it later the same day; doses should not be doubled to make up for a missed capsule. Pomalid treatment is usually continued in repeating 28-day cycles for as long as clinical benefit is observed and side effects remain manageable, or until your haematologist decides to change therapy.
Precautions
Pomalidomide is structurally related to thalidomide and carries a significant risk of causing severe birth defects if taken during pregnancy. Because of this, strict contraceptive measures are mandatory for women of childbearing potential and for men with partners who could become pregnant, both during treatment and for a defined period after the last dose, according to local regulations. Pomalid must never be used in pregnancy, and breastfeeding is generally not recommended while receiving pomalidomide.
Pomalid can lower white blood cell and platelet counts, increasing the risk of infections and bleeding. Regular full blood counts are required before and during treatment, and dose adjustments or temporary interruptions may be needed if neutropenia or thrombocytopenia develops. There is also an increased risk of venous thromboembolism, especially when pomalidomide is combined with dexamethasone, so your doctor may recommend anticoagulant prophylaxis depending on your risk profile. Other precautions include monitoring kidney and liver function, watching for signs of neuropathy, and reviewing all concurrent medicines to avoid problematic interactions.
Pomalidomide Side Effects
Common side effects
Common pomalidomide side effects include fatigue, weakness, anaemia-related tiredness, constipation or diarrhoea, nausea, decreased appetite, mild peripheral neuropathy such as tingling or numbness in hands and feet, muscle cramps and mild rash or skin dryness. Laboratory tests may show low neutrophil and platelet counts, as well as modest changes in kidney or liver blood tests. Many of these effects can be managed with supportive medicines, dose delays or reductions, and close monitoring in the clinic.
Serious side effects
Serious pomalidomide adverse effects require urgent medical attention and often prompt treatment modification. These include febrile neutropenia or any fever in the context of low white blood cell counts, signs of severe infection such as chills, persistent cough, shortness of breath or confusion, major bleeding or unexplained bruising due to severe thrombocytopenia, and symptoms of venous thrombosis or pulmonary embolism such as leg swelling, chest pain or sudden breathlessness. Severe skin reactions with widespread rash, blistering or peeling, pronounced liver dysfunction with jaundice or dark urine and severe allergic reactions also require immediate assessment. Any sudden or severe symptom while taking Pomalid should be reported to your haematology team or emergency services without delay.
Storage
Pomalid 2 mg and 4 mg capsules should be stored at room temperature, usually below 25 °C, in a dry place away from direct heat and light. Keep the capsules in their original blister strips and outer carton until the time of use to protect them from moisture and to avoid mix-ups with other medicines. As pomalidomide can be harmful if handled or ingested by others, especially pregnant women, the pack must be kept out of sight and reach of children and pets. Unused or expired capsules should not be thrown in household rubbish; instead, your pharmacist or clinic can advise on safe disposal according to local regulations.
Why Buy from Generic Meds Mart
Generic Meds Mart helps patients and clinics access Pomalid pomalidomide capsules in regions where availability, pricing or supply chains may be challenging. We source Pomalid 2 mg and Pomalid 4 mg only from licensed manufacturers and authorised distributors that follow Good Manufacturing Practice standards and maintain traceable batch and expiry records. By supplying capsules in original, sealed packaging, we enable hospital and clinic pharmacies to verify the brand, strength and batch numbers against prescriptions and treatment protocols.
All orders are processed in USD through secure online checkout, and shipments are prepared in neutral outer packaging that does not refer to multiple myeloma, chemotherapy or pomalidomide. Where offered by our logistics partners, trackable delivery options allow you and your haematology team to plan ahead and avoid unnecessary treatment interruptions due to supply issues. Generic Meds Mart provides access and logistical support only; all decisions about whether pomalidomide is suitable, what pomalidomide dosage should be used and how long treatment should continue remain entirely with your specialist team.
Order Now
Before you buy Pomalid online from Generic Meds Mart, you should already have a confirmed diagnosis of multiple myeloma and a clear written treatment plan from your haematologist that includes pomalidomide, the intended daily dose, the number of cycles and the required safety monitoring. Your doctor will consider prior treatments, response durations, organ function, infection risk and thrombotic risk before recommending Pomalid-based therapy. Once your regimen has been agreed, you or your clinic can calculate how many packs of Pomalid 2 mg and 4 mg are needed for each cycle and select the appropriate strengths when placing an order.
You should never start, stop or change pomalidomide dosage on your own, nor switch between Pomalid 2 mg and 4 mg without direct guidance from your haematology team. If you develop new symptoms, infections, unexplained bruising, breathlessness, chest pain, sudden swelling or any other alarming problems while on Pomalid, seek urgent medical advice rather than adjusting treatment yourself. Generic Meds Mart’s role is to help ensure timely, discreet and verifiable supply of the pomalidomide strengths prescribed for you; all clinical decisions about multiple myeloma management must remain with your specialists.
FAQ about Pomalid (Pomalidomide)
Q1: What is Pomalid used for in multiple myeloma?
Pomalid contains pomalidomide, an immunomodulatory agent used with dexamethasone in adults with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma who have already received prior lines of therapy. It is designed to further control myeloma activity when earlier treatments are no longer effective or appropriate, under the supervision of a haematologist.
Q2: How long will I stay on Pomalid treatment?
The duration of Pomalid treatment varies between patients. Many people continue pomalidomide in repeating 28-day cycles for as long as their myeloma remains controlled and side effects are manageable. Your haematology team will review blood counts, organ function, symptoms and response markers regularly and will decide whether to continue, adjust or discontinue therapy based on these findings.
Q3: What should I do if I miss a dose of Pomalid?
If you miss a dose of Pomalid, do not take a double dose to make up for it. Your clinic will usually advise you to take the missed capsule later the same day if there is enough time, or to skip it and continue with the next scheduled dose. The exact advice may differ depending on your protocol, so you should follow the instructions provided by your haematology team and inform them of any adherence problems.
Q4: Can I drive or work normally while taking Pomalid?
Some people can continue driving and working while on pomalidomide, but fatigue, dizziness, neuropathy or other side effects may affect concentration and physical abilities. Until you know how Pomalid affects you, it is sensible to be cautious with activities that require full alertness. If treatment makes you feel very tired, dizzy or unsteady, discuss this with your doctor, who may suggest adjustments to your work, driving or dosing schedule.
Q5: Is Pomalid the same as thalidomide or lenalidomide?
Pomalid is related to thalidomide and lenalidomide, and all three are immunomodulatory agents used in multiple myeloma, but they are not identical medicines. Pomalidomide has a different potency, dosing, side effect profile and evidence base compared with the other IMiDs. Your haematologist will choose between these options, or use them sequentially, according to your previous treatments, response patterns and overall clinical situation. You should never substitute one for another without specialist advice.
Be the first to review “Pomalid 2 mg, 4 mg Pomalidomide Capsules” Cancel reply
You may also like…
Related products
Anticancer






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.